How to create binary search tree in javascript with ES6 classes
javascript data-structure interview es6 bst binary-tree binary-search-tree english
Intro
In this post, I'd like to share my implementation of Binary SearchTree (BST) in JavaScript using mechanism of ES6 Classes.
Binary Search Tree
Binary Search Tree is a node-based binary tree data structure which has the following properties: 1. The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key. 2. The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key. 3. The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree. BST ref (geeksforgeeks)
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(data) {
this.root = {
data: data,
left: null,
right: null
};
}
// Time complexity:
// In case of balanced tree: O(log N)
// worst case O(n)
insertTo(node, key) {
if (key < node.data) {
if (node.left) {
this.insertTo(node.left, key);
return;
} else {
node.left = new Node(key);
}
} else {
if (node.right) {
this.insertTo(node.right, key);
return;
} else {
node.right = new Node(key);
}
}
}
}
Node
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
How to use it
let bst = new BinarySearchTree(0);
// add some nodes
bst.insertTo(bst.root, 2);
bst.insertTo(bst.root, 1);
bst.insertTo(bst.root, 3);
bst.insertTo(bst.root, 4);
Find element in BST
// Time complexity:
// In case of balanced tree: O(log N)
// worst case O(n)
function findIn(node, key) {
if (node.data === key) {
return node;
}
if (key < node.data) {
return node.left
? findIn(node.left, key)
: null;
} else {
return node.right
? findIn(node.right, key)
: null;
}
}
Tree Traversals
Preorder
- Visit the root.
- Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Preorder(left-subtree)
- Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Preorder(right-subtree)
Iteratinve method:
function preorder() {
let currNode = this.root;
let stack = [];
stack.push(currNode);
while(stack.length || currNode) {
currNode = stack.pop();
console.log(currNode.data);
if (currNode.right) {
stack.push(currNode.right);
}
if (currNode.left) {
stack.push(currNode.left);
}
}
}
Recursive method:
function recursivePreorderTraversal(node) {
if (node.data) {
console.log(node.data);
}
if (node.left) {
recursivePreorderTraversal(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
recursivePreorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
Inorder
- Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(left-subtree)
- Visit the root.
- Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(right-subtree)
Iteratinve method:
function inorder() {
let currNode = this.root;
let stack = [];
while(stack.length || currNode) {
if (currNode) {
stack.push(currNode);
currNode = currNode.left;
} else {
currNode = stack.pop();
console.log(currNode.data);
currNode = currNode.right;
}
}
}
Recursive method:
function recursiveInorderTraversal(node) {
if (node.left) {
recursiveInorderTraversal(node.left);
}
if (node.data) {
console.log(node.data);
}
if (node.right) {
recursiveInorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
Postorder
- Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Postorder(left-subtree)
- Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Postorder(right-subtree)
- Visit the root.
Iteratinve method:
function postorder() {
let currNode = this.root;
let stack = [];
let lastVisited = null;
while(stack.length || currNode) {
if (currNode) {
stack.push(currNode);
currNode = currNode.left;
} else {
let peekNode = stack[stack.length - 1];
if (peekNode.right && lastVisited !== peekNode.right) {
currNode = peekNode.right;
} else {
console.log(currNode.data);
lastVisited = stack.pop();
}
}
}
}
Recursive method:
function recursivePostorderTraversal(node) {
if (node.left) {
recursivePostorderTraversal(node.left);
}
if (node.data) {
console.log(node.data);
}
if (node.right) {
recursivePostorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
Breadth-first search
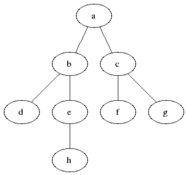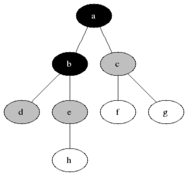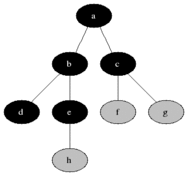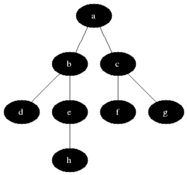
function breadth() {
let currNode = this.root;
let queue = [];
queue.push(currNode);
while(queue.length) {
currNode = queue.shift();
console.log(currNode.data);
if (currNode.left) {
queue.push(currNode.left);
}
if (currNode.right) {
queue.push(currNode.right);
}
}
}
JSFiddle
<script async src="//jsfiddle.net/gudobw9n/11/embed/js/dark/">
Happy creating your own binary search trees! :)